Cache in HTTP
Caching is a technique that stores a copy of a given resource and serves it back when requested
Terminologies
- Removing from Cache is called Eviction
- Cache before expiration time is called Fresh
- Cache after expiry is called Stale
Advantages - reduces latency & network traffic
Summary about Caches
Types of caches - private (browser), shared/proxy caches (ISP level), gateway (CDN)
HTTPS won't be cached by shared caches
Cache is fresh (server without checking server) if expiry time set, and is still within the fresh period. A request for a stale resource will be forwarded with If-None-Match to check if it is in fact still fresh. If so, the server returns a 304 (Not Modified)
If stale, the origin server will be asked to validate it. It won't be evicted or ignored
Scenarios like disconnected from a network — a cache can serve stale responses without checking with the origin server
Cache-Control
The Cache-control header for defining cache policy
| Cache Control Header | Usage |
|---|---|
| no-store | Don't Cache |
| no-cache | Cache but revalidate |
| private | can be stored in browser |
| public | can be stored anywhere |
| max-age=seconds | max time a resource will be considered fresh |
| s-maxage | similar to max-age but only for shared |
| must-revalidate | expired ones should not be used |
| proxy-revalidate | similar to must revalidate but only for shared |
| stale-while-revalidat | can use the current (stale) version while it re-fetches the latest version in the background |
| stale-if-error | use stale is refetch fails |
*If both Cache-Control and Expires present, Cache-Control takes precedence
Cache validation
If Cache-control: must-revalidate present or If the Cache is expired, Cache will be validated with server
ETag - opaque-to-the-useragent - strong validator If ETag present, the client can issue an If-None-Match in the header of future requests to validate the cached resource
Last-Modified - a weak validator If present client can issue an If-Modified-Since request header to validate the cached document
On validation, server can response with a normal 200 OK, or it can return 304 Not Modified (with an empty body)
Best practices
If Cache implemented, page visit stats may get affected. To solve it use 1x1 transparent uncacheable image for every page
- Perfect for Cache - 200 (OK), 301 (Moved Permanently), 404 (Not Found)
For frequently changing content like train live status, use no-cache
For contents that are static, use cache with long life time
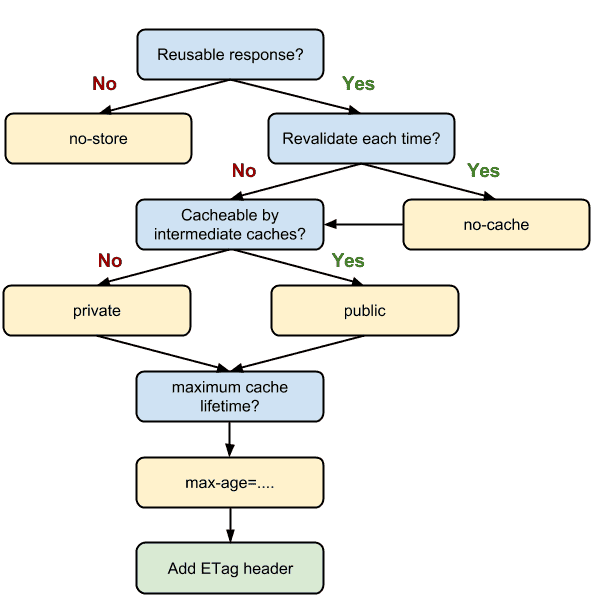
Source: https://sitebulb.com/media/2002/http-cache-decision-tree.png
Reference:
https://developer.mozilla.org/en-US/docs/Web/HTTP/Caching
https://jakearchibald.com/2016/caching-best-practices/